TEC 5323 Advanced Database Technology
Oracle Enterprise Manger (EM)
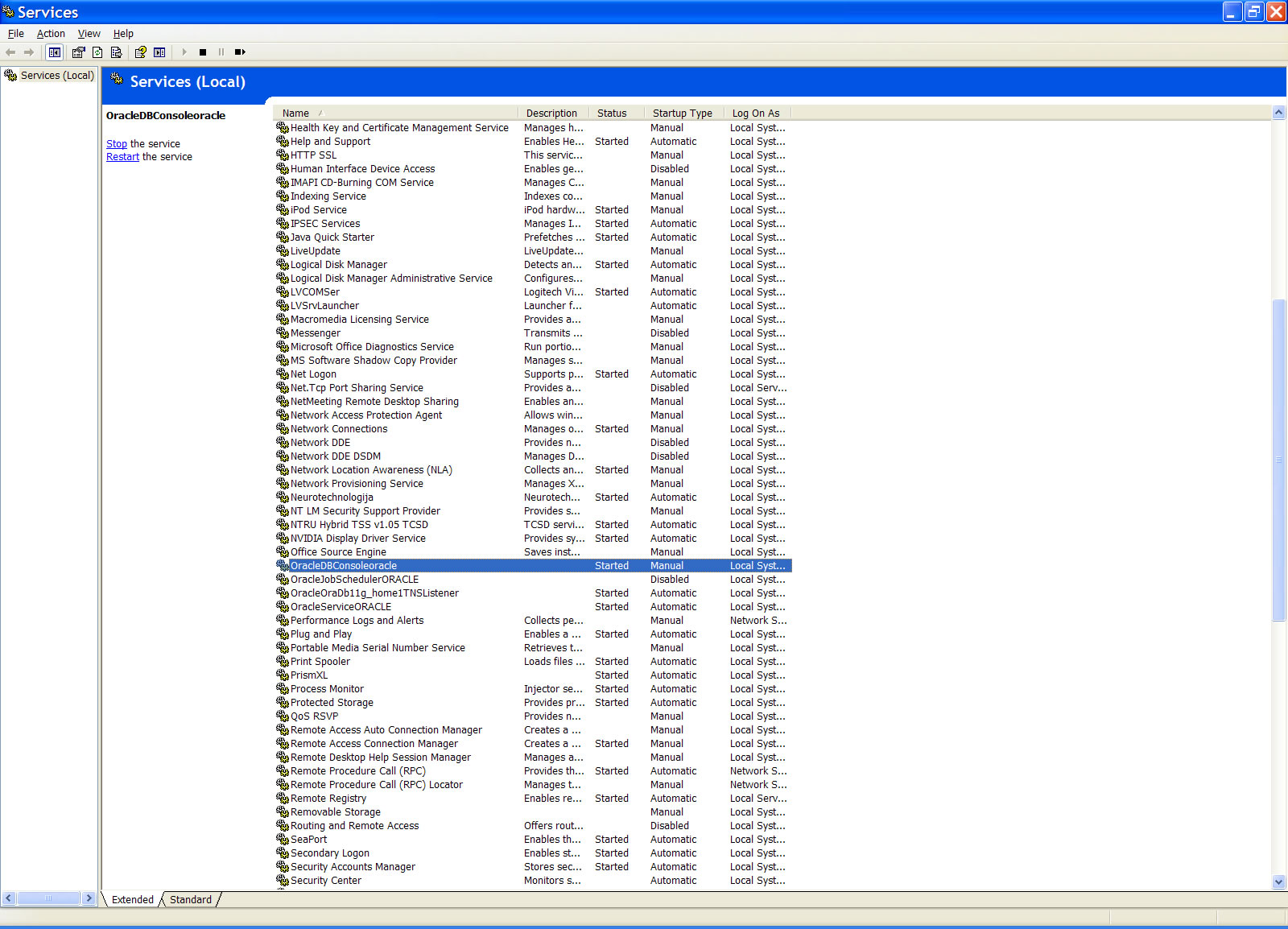
Oracle Enterprise Manager (referred to as Enterprise Manager or EM) is the Oracle integrated management solution for managing the complete Oracle environment. All services within your enterprise, including hosts, databases, listeners, application servers, HTTP Servers, and Web applications, are easily managed as one cohesive unit. When you install an Oracle database, the Oracle Universal Installer also installs the Oracle Enterprise Manager. The Web-based Database Control serves as a tool for managing your Oracle database. From the Oracle Enterprise Manager, you can perform administrative tasks such as creating schema objects (tablespaces, tables, and indexes), managing user security, backing up and recovering your database, and importing and exporting data. You can also view performance and status information about your database instance. From the Oracle Enterprise Manager, you can perform administrative tasks such as creating schema objects (tablespaces, tables, and indexes), managing user security, backing up and recovering your database, and importing and exporting data. You can also view performance and status information about your database instance. Starting EM Service (dbconsole) in WindowsAfter successful installation of Oracle10g, Windows will start EM service automatically when the computer is started. If it does not start automatically, you can start the EM service (dbconsole process) as follows. To start EM service (dbconsole) as a service:
You can also use the Services page to stop the EM process. The following illustrates how it looks like for Oracle 11g. (8/2/2011)
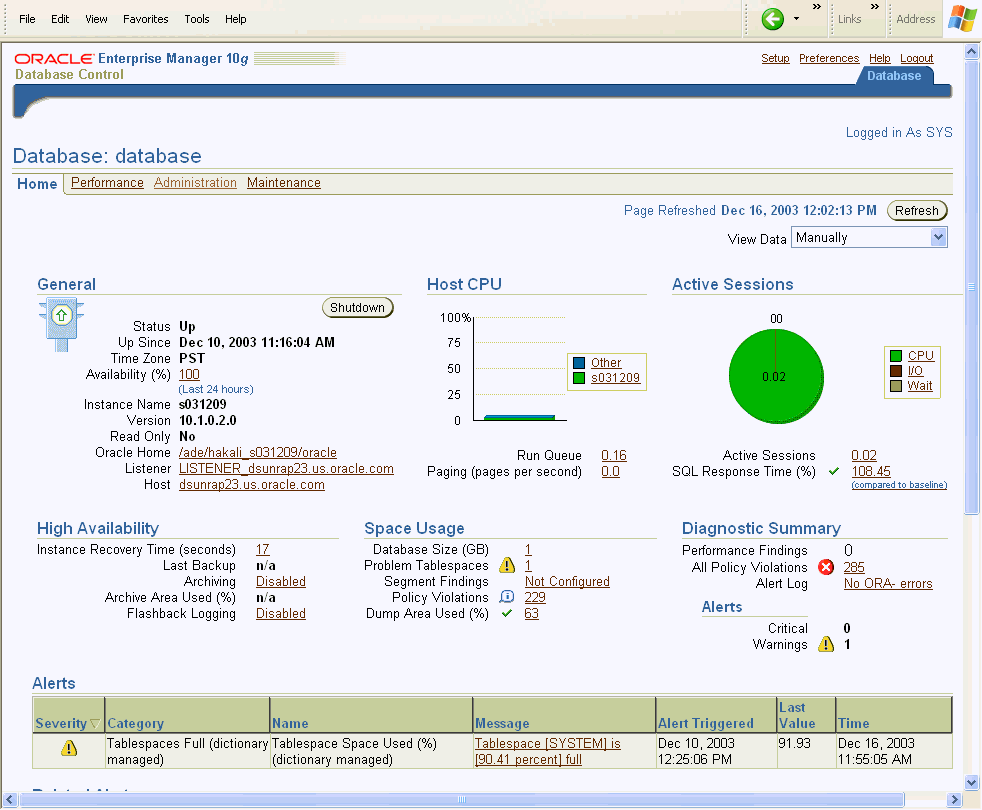
Accessing the Oracle Enterprise ManagerAt the end of a successful database creation, Oracle Enterprise Manager is automatically launched and the database is started. At other times, provided the dbconsole process is running on the server, you can navigate to your Database Control from your client browser as follows:
The property pages across the top of the page enable you to access performance, administration, and maintenance pages for managing your database. The functionality provided by these pages is discussed in other chapters of this book. The various sections of the Database Home page, and related links, provide a wealth of information about the database's environment and health. For example, the Alerts , Related Alerts , and Performance Analysis sections warn you of errors and performance problems that are impacting the operation of your database. You can click the provided links to see more detail about the problem area, and even to obtain recommendations for resolving the problem. Please click here to go to Oracle's web site to learn more details on Oracle Enterprise Manager. |