|
|
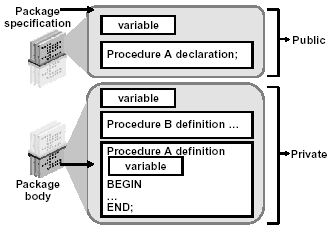
You create a package in two parts:
- The package specification is the interface to your applications. It declares the public types, variables, constants, exceptions, cursors, and subprograms available for use. The package specification may also include PRAGMAs, which are directives to the compiler.
- The package body defines its own subprograms and must fully implement subprograms declared in the specification part. The package body may also define PL/SQL constructs, such as types variables, constants, exceptions, and cursors.
|
Private components are placed in the package body and can be referenced only by other
constructs within the same package body. Private components can reference the package public
components. |
|
|
Public components are declared in the package specification. The specification defines a public
application programming interface (API) for users of package features and functionality. That is,
public components can be referenced from any Oracle server environment that is external to the
package. |
|
Public components
Private Components
|